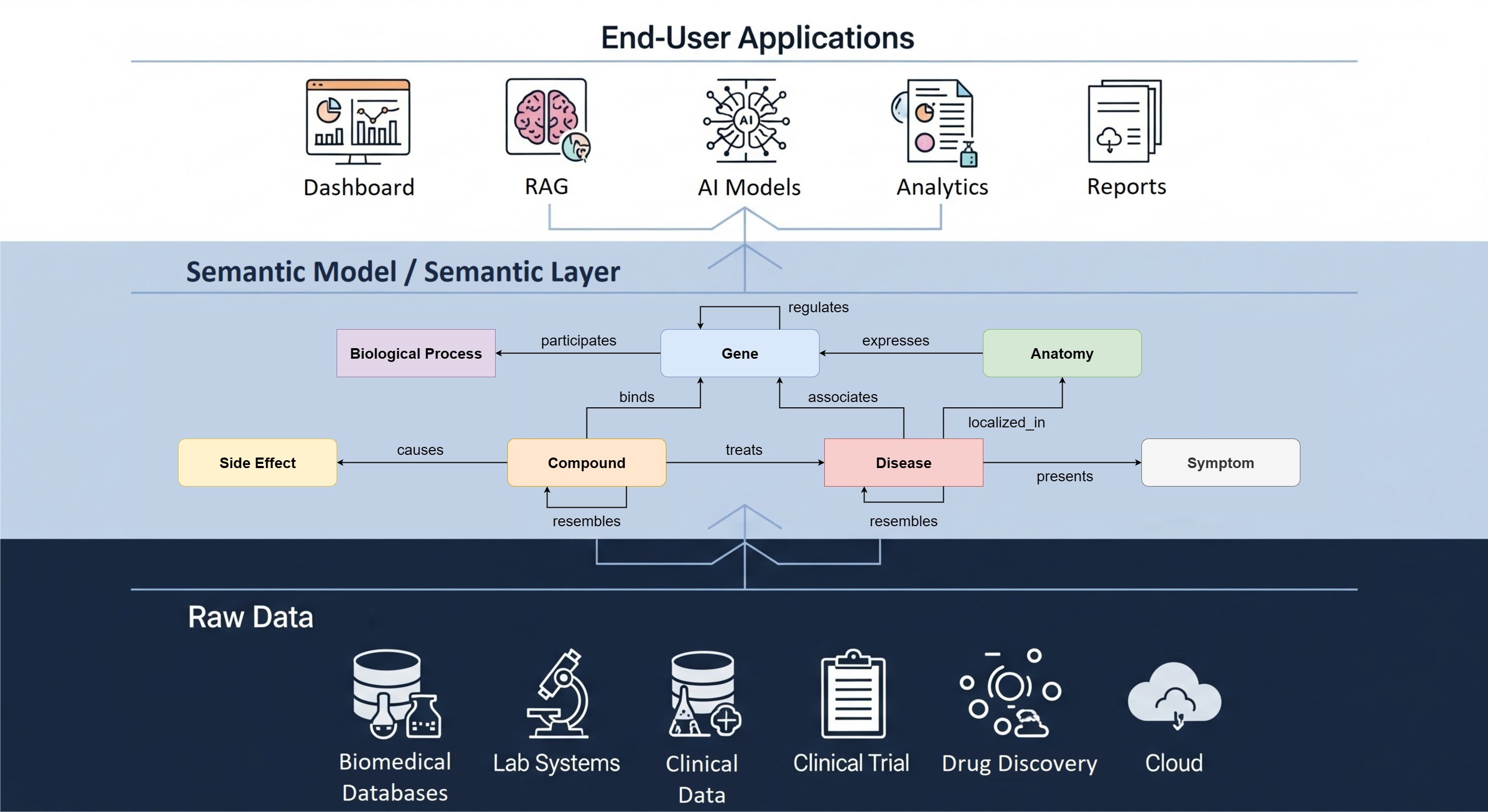
The IMI RADAR-AD project aims to develop a digital platform to remotely collect data from smartphone applications, wearable devices and fixed home-based sensors to track subtle changes in cognitive abilities and behaviour that could be an indication of the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. After an initial phase of identification of relevant functional domains and corresponding data streams by clinical experts, a number of wearable devices and other sensors have been selected to facilitate the detection of early-stage symptoms of Alzheimer's disease.
The studies will be supported by the RADAR-base digital platform, which was developed within the framework of the IMI RADAR-CNS project and is available as open-source software published under the Apache License Version 2.0. For RADAR-AD the platform will be adapted to help answer the project-specific research questions.
The RADAR-base platform is an end-to-end solution to collect, manage and store sensor data from smartphones and wearable devices to enable remote monitoring of study participants and decentralized clinical trials. The platform supports multiple devices and can be used for a range of disease areas as its modular plugin-based architecture allows for simple and fast extension and customization.
In close collaboration with our partners from Oxford’s Big Data Institute and from King’s College London, The Hyve’s expert team of RADAR-base software developers has customized the RADAR-base platform to comply with the study protocols created by the RADAR-AD consortium.

Integration of additional data streams
The team of software engineers also developed integrations for a number of other devices and applications that should enable researchers to track subtle changes in cognitive ability and physical activity. Examples are:
- Altoida app for assessment of Brain Health
- Axivity 3 device to collect 3D accelerometer data
- Physilog device from Gait Up to identify changes in the individual’s gait
- Mezurio app developed at the University of Oxford to complete interactive, scientifically valuable measurement tasks
- Banking app developed by the Centre for Research and Technology Hellas (CERTH) to simulate simple calculations and transactional tasks
Besides extension of the data-ingestion options for RADAR-base, we have also added support to deploy RADAR-base using Kubernetes, which is an open-source container orchestration system for automating application deployment, scaling, and management. The adapted platform was deployed in a high-computing cluster in Oxford, leveraging Kubernetes to ensure robustness and scalability.
We are very much looking forward to seeing the results of the first studies that will be running in multiple sites. To read more about the project or the RADAR-base platform, please visit: