Context
As part of the cBioPortal Spring Hackathon 2025, the team from The Hyve developed an exciting new feature: the AI OQL-Helper, which takes in natural language and produces Onco Query Language (OQL) commands. This smart chat interface is now available for testing on The Hyve demo server. It is embedded directly into the cBioPortal Query page, allowing users to write queries in natural language. The AI then translates these into Onco Query Language (OQL) commands, making advanced genomic data querying accessible to everyone.
How it works
- Log in to The Hyve cBioPortal demo instance using any method you prefer.
- Select a study from the study list.
- Click Query by Gene and scroll down to find the Ask AI OQL Helper dropdown.
- Enter your query in plain language and click Generate Query.
- Review the generated query, then submit it to launch the results page as usual.
This lowers the barrier for users new to OQL, letting you explore complex data quickly and intuitively.
Example queries
Using the Brain Lower Grade Glioma study from TCGA PanCan Atlas, here are some natural language query examples:
- Show me all data for TP53, KRAS, and IDH1
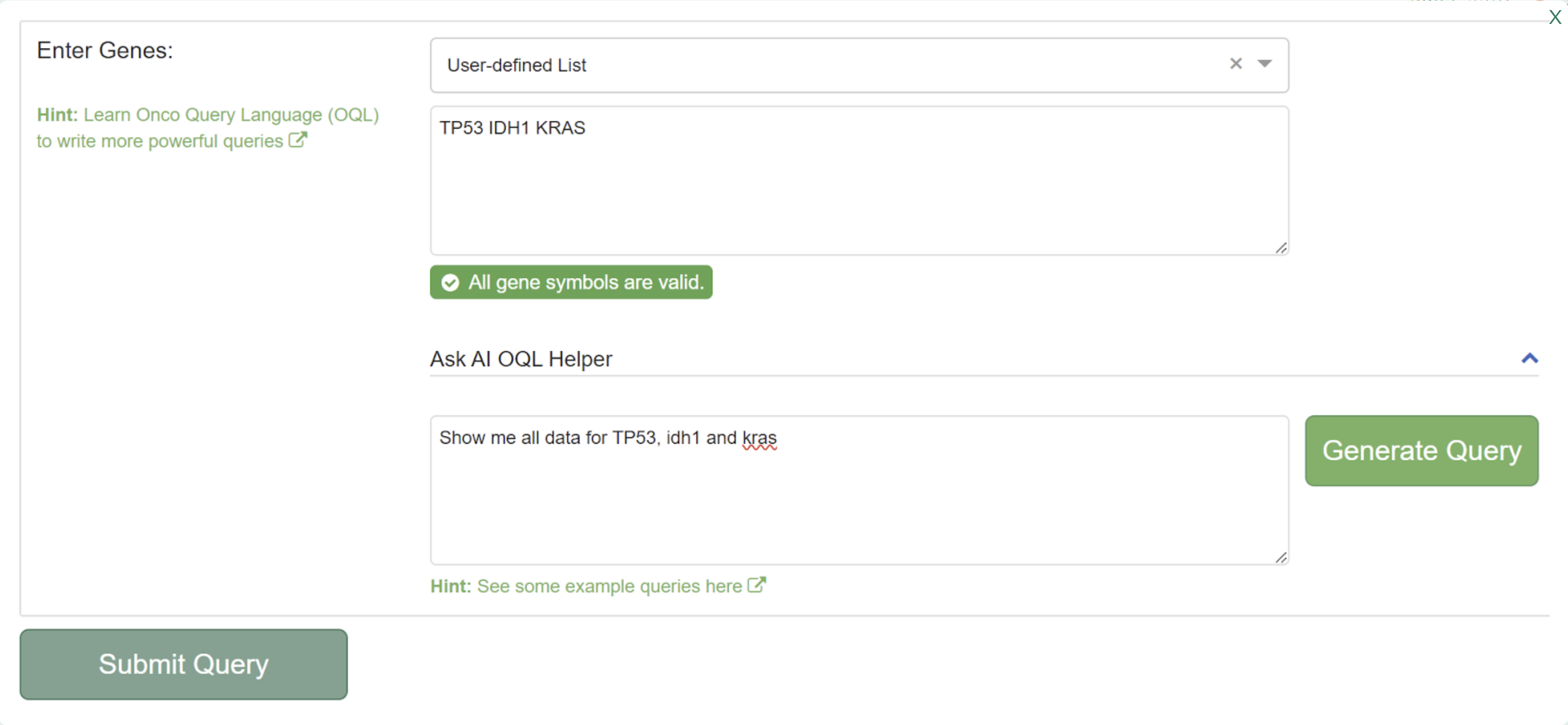
Notice how the natural language request is translated into the default query syntax: TP53 IDH1 KRAS, which is the simple way to query for all mutations, amplifications, homozygous deletions, and fusion events in the queried genes. Submit the query to go to the Results Page.
- Query EGFR amplifications
In this example, the AI Helper translates the plain query into the OQL syntax using the AMP keyword for the EGFR gene.
- Show BRAF V600E mutations
Here we are specifically querying for valine (V) to glutamic acid (E) alterations at position 600 in the BRAF gene with the help of AI. See the results here.
- Show me somatic missense mutations in PIK3CA
To query for only somatic missense mutations, AI Helper generates a query by combining the two keywords, successfully applying the OQL syntax.
- Show me KRAS mutations in positions 12 and 13
KRAS mutations at codons 12 and 13 are known hotspots in cancer. Users often query for these alterations using cBioPortal. The OQL Helper enables users to generate queries without needing to know the rules of the OQL syntax. Results confirm that the query indeed filters for alterations at codons 12 and 13.
More complex queries
- All BRAF mutations except those at V600 and all TP53 mutations except missense
OQL can also be used to filter out some specific alterations from your queries. The new AI OQL Helper successfully eliminates the BRAF V600 mutations and TP53 missense mutations from the search.
- Query IDH1 R132H and R132C mutations in separate groups, give groups these names respectively "132H" and "132C"
OQL can be used to group some genes and alterations in OncoPrint tracks with custom names. This requires proper syntax knowledge. However, simply describing the grouping requirements to the new AI OQL Helper will create those groups for you. In the results page of this query, you will see the tracks with appropriate labels.
- Query genes that are important in brain tumor diagnosis
We also tested the new AI OQL Helper for its knowledge on general cancer genomics. In this case, by querying for important genes in brain tumor diagnosis. You can see below that the response included some faulty gene IDs, which are then flagged by the cBioPortal’s native syntax corrector in red, already with suggestions to correct the faulty gene IDs.
When the corrections are applied to the generated query, we can continue to query and to explore the distribution of alterations in important genes in brain tumors.
Error Handling
If the user submits a natural language text that does not relate to the context of query generation in cBioPortal OQL, the AI OQL Helper sends a warning message, asking the user to send a valid request.
We want to hear your feedback!
Try this new feature yourself on the demo server. The AI generates the correct OQL instantly, so you can focus on insights rather than syntax.
Note: This is an experimental feature. Please test it out and share your feedback with us (feedback@thehyve.nl) — including the queries you have tried and whether the responses matched your expectations. Your input will help us improve the AI OQL-Helper!