The Hyve can look back on a productive and prominent year for RADAR-base as we reached a number of important milestones. We have made significant improvements to the platform and many partners of RADAR-CNS have incorporated RADAR-base in their studies. Along the way, we received a prestigious award, published well-received publications and enjoyed much interest in the platform at events and conferences where RADAR-base was showcased.
In this blog, we would like to highlight important developments on the RADAR-base platform in 2018, including some interesting facts from ongoing studies that are currently using the platform and upcoming collaborations for 2019.
The platform
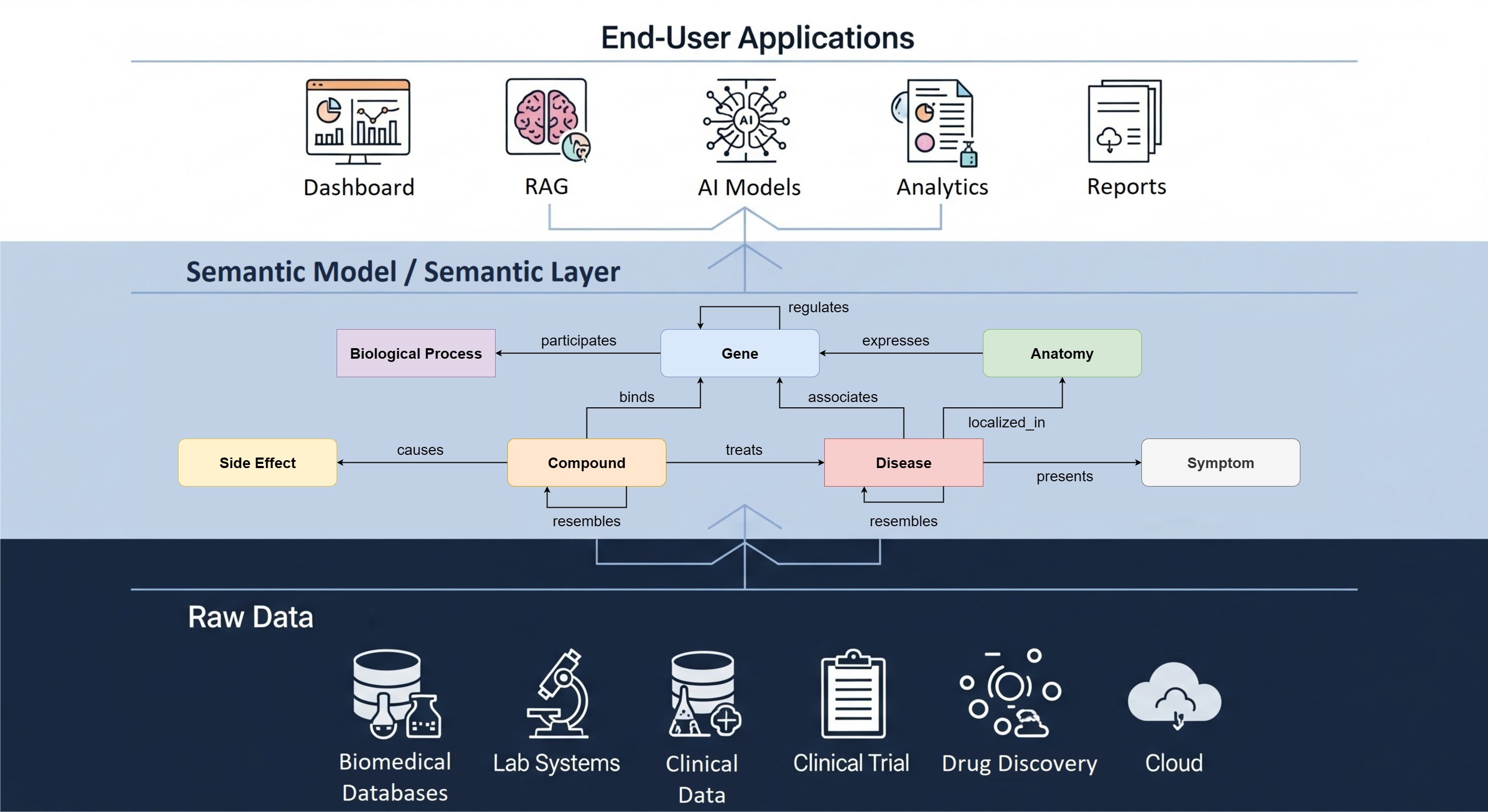
RADAR-base is an award-winning open-source platform that enables scientific research with sensor data from smartphones and wearable devices. The platform facilitates remote monitoring of patients using eHealth and mHealth technologies. Continuous remote monitoring not only gives health care professionals more insight into the health status of patients between hospital visits, but it also potentially enables early detection of relapse, enabling early intervention during incidents.
The wearable sensor data collection platform can be used for a broad range of diseases. The platform supports passive remote monitoring from wearable devices and a pRMT app to passively access sensor data from smartphones. Active remote monitoring is supported by an aRMT app for patient reported outcomes (PRO), questionnaires and active tests on smartphones.
RADAR-base has been designed and developed with extensibility in mind, such that it provides seamless integration with various wearable devices, both medical and consumer grade. It allows for multiple devices to be used simultaneously in a study and retrieval of harmonised data from all of these devices. Besides, the advantages of the platform being open-source are tremendous, allowing usage of the platform without licensing cost. Therefore, The Hyve is proud to be contributing to its development.

Official launch
The RADAR-base platform (Remote Assessment of Disease And Relapse-base) was developed in the framework of the RADAR-CNS project, a public-private partnership funded by the Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) which brings together 23 organizations from academia and industry. You will read more about the project and ongoing studies later in this blog. The Hyve has been actively involved in the RADAR-CNS project since its official kick-off in 2016. We collaborate closely with other partners including King’s College London (KCL), Janssen Pharmaceuticals, UCB, Biogen, University of Freiburg, Lundbeck, Lygature, and Vibrent Health. The technical platform was officially launched under the name of RADAR-base in April 2018.
Best of Show Award at Bio-IT World
RADAR-base won the prestigious Best of Show Award in the category Data Integration & Management at the annual Bio-IT World Conference 2018 in Boston (15-17 May). This event brings together all major stakeholders in the field of bioinformatics, including academia and industry. RADAR-base was presented to a panel of expert judges at the event by Ward Weistra and he received the Best of Show Award on behalf of the entire RADAR-base team.

Developments on the RADAR-base platform
In the past year, The Hyve and its collaborating partners, have continued to expand the RADAR-base platform and made it more robust and user-friendly. One of the highlights is support for the FitBit Charge 2, one of the most popular fitness trackers on the market. This addition significantly increases the opportunities for RADAR-base to be used by a larger number of people. By collecting data from third party Cloud-based APIs, it also validates another data ingestion method of RADAR-base.
We have also integrated the Bittium eFaros, a wearable device for electrocardiogram (ECG) and heart-rate variability (HRV) monitoring. Furthermore, a highly adaptable sensor data visualisation dashboard was developed in collaboration with King’s College London and Intel, which allows researchers to visualize sensor data and monitor compliance for every participant real-time. Just as importantly, we have taken measures to make RADAR-base GDPR compliant.

Ongoing RADAR-CNS studies
The RADAR-CNS consortium partners are the initial users of the RADAR-base platform. They use it for studies on disorders related to the central nervous system (CNS) such as Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and Epilepsy.
King’s College London (KCL) and the University of Freiburg have conducted in-hospital epilepsy studies using wearable devices and the pRMT app with concurrent EEG and video recordings. More than 140 participants have joined the studies so far. You can read about the object and outcome of the study in this publication.
Major Depressive Disorder studies are being conducted by KCL and CIBER using both pRMT and aRMT apps in combination with FitBit Charge 2 devices for remote data collection. Vrije University Medical Center Amsterdam (VUmc) will start recruiting participants for another MDD study in January 2019.
Studies on participants with Multiple Sclerosis are being conducted at Vall d'Hebron Research Institute (VHIR), Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, and RegionH where various measurements are taken to investigate disability and fatigue related to MS and the occurence of depression in MS patients. These studies include aRMT and pRMT smartphone apps in combination with eFaros and Fitbit Charge 2 devices.
So far, we have recruited more than 380 participants from all sites and gathered more than 3 TB of raw data for retrospective analysis. Currently, some of the RADAR-CNS partners are evaluating the data collected to identify patterns and to answer research questions.

Events and Responses
RADAR-base was well-received at many events around the world such as BioIT World 2018 in Boston, New Scientist Live event in London, Ubicomp 2018 in Singapore, MindTech National Symposium and Singelloop 2018 in Utrecht. Live demonstrations of RADAR-base attracted huge interest. Efforts to make the platform open-source were highly appreciated.

RADAR-AD Project Kick off
We welcome the new year with another exciting study for the platform. The RADAR-AD project, another IMI2 funded project to investigate the potential of remote assessment of patients for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. The Hyve is proud to be a partner of the RADAR-AD project. Its goal has been described as follows:
“The development of objective and sensitive functional measures will enable potential dementia therapies to demonstrate functional impact and clinical meaningfulness of early intervention without requiring long follow-on studies thus reducing time and cost required to bring Alzheimer’s disease modifying drugs to market.”
The project kick-off is scheduled to take place in London by the end of January.
Conclusion
All in all, we can look back on an amazing year with RADAR-base. Thanks to all partners who contributed to this success.
At the same time, RADAR-base remains very much an ongoing project. We are sure to incorporate new features in 2019 and further develop and improve the platform so that it performs even better in clinical practice and large-scale environments.
If you want to learn more about the platform, please check out our online try-it-out demo. Read our previous blogs to learn more about RADAR-base and updates.
If you’re interested in setting up a wearables study with RADAR-base, please contact The Hyve for advice. Last, but not least, we welcome any feedback and questions and wish you a Happy New Year!
Funding statement and Disclaimer
The RADAR-CNS project has received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking under grant agreement No 115902. This Joint Undertaking receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and EFPIA.
This communication reflects the views of the RADAR-CNS consortium and neither IMI nor the European Union and EFPIA are liable for any use that may be made of the information contained herein.